
Nuclear reactors may be closed for four main reasons: they reached their end of life, they had an accident, they had technical problems and couldn’t be repaired, or a political decision made them close. In this article, I review the closure reasons for 19+ nuclear reactors.
This article is part of a series on the DEC Report. The DEC report is a 200+ pages freely accessible report I wrote on climate change and energy. It assesses the world’s potential to tackle climate change by removing GHG emissions in energy and agriculture, and it assesses how we can optimize this transition.
- ➡️➡️ The DEC Report (pdf)
- 🌊 Hydropower potential (1/8)
- ☀️ Solar potential (2/8)
- 🌬️ Wind potential (3/8)
- 🏭 Nuclear potential (4/8)
- 🛢 How much fossil fuel do we consume each year? (5/8)
- 🔥 Energy, EROI and limits to growth (6/8)
- ☢️ How many people died because of the Chernobyl disaster? (7/8)
- ⚡ Why do we close nuclear reactors? (8/8)
Closure reasons
Closure reasons for most of nuclear reactors were reviewed.
Closure for political reasons include:
- closing nuclear reactors instead of fossil fuel power plants (coal, gas, oil) while the reactor could continue to work,
- closing nuclear reactors for cost reasons in a context where fossil fuels are cheaper (closing nuclear reactors to use gas instead because gas would be cheaper),
- closing nuclear reactors for excessive security constraints in a context where alternatives such as coal are kept and are more deadly,
- closing nuclear reactors after a vote, after a political opposition or after protests.
Political reasons do not include:
- closing >40y.o. nuclear reactors by substituting them with a low-carbon alternative,
- closing nuclear reactors which had issues by substituting them with another more recent nuclear reactor,
- closing nuclear reactors which had issues and an independent authority stated that the reactor couldn’t be repaired for industrial reasons.
Accidents include:
- meltdowns, fires, etc.
19 Nuclear reactors and their closure reason
Kozloduy NPP

Kozloduy NPP (Nuclear Power Plant) was closed for political reasons, it was a requirement of the EU to let Bulgaria enter the EU. Kozloduy produced 16 TWh of low-carbon electricity per year. Nowadays, Bulgaria is instead consuming a lot of coal to produce electricity, while coal is responsible for thousands of deaths each day on the planet.
Gentilly NPP
Gentilly NPP was decommisionned for economic and political reasons in a context where fossil fuels are cheaper and still in use, without considering climate issues.
Fukushima Daini
Fukushima Daini (not to be confused with Fukushima Daiichi) was closed for political reasons in a context where fossil fuels are still widely used in Japan and are much more dangerous to health than nuclear energy. The plant was safe and under control after the 2011 Earthquake in Japan.

Ikata NPP
The Ikata 1 and 2 reactors have been closed for political and economic reasons in a context where fossil fuels were cheaper and without considering climate issues.
Ōi NPP
The Ōi 1 and 2 reactors have been closed for safety reasons in a context where fossil fuels are more deadly and still used; and without considering the dangers climate change will represent for humanity in the future in a situation where this plant could be used to reduce the use of fossil fuels.
Onagawa NPP
Onagama NPP has been closed for safety and economic reasons, stating that the reactor was “unprofitable”, in a context where fossil fuels are cheaper, more deadly, without considering the dangers climate change will represent for humanity.
Bohunice

Bohunice 1 and 2 have been closed as a condition of accession into the European Union. Slovakia was required to deactivate the two reactors at the V1 plant, without considering climate change issues.
Kori
The Kori NPP was closed by Korea in 2017 for political reasons, starting “a journey to becoming a nuclear-free nation”, while South Korea is still consuming fossil fuels, while this reactor could have been used to consume less fossil fuels, without considering the dangers climate change will represent for humanity. Safety reasons were cited: “Elements that might pose any threat to the lives, safety and health of the people should be gotten rid of in the policies that we make”, ignoring a hierarchy of risks which includes deaths from the use of fossil fuels (fine particles) and deaths related to climate change which will affect all countries of the world including South Korea.
Wolsong
The Wolsong NPP was closed for political reasons “as part of the long-term scheme to phase out nuclear power”, while South Korea is still consuming fossil fuels, while this reactor could have helped in reducing this consumption, ignoring all risks related to climate change.

Jinshan
Jinshan NPP was decommissioned for political reasons. The unit has been idle for almost three years before 2018 following a fuel fault which has been rectified. Despite having regulatory approval to operate, its restart has been blocked politically. Taiwan’s Democratic Progressive Party was elected with a policy of creating a “nuclear-free homeland”, ignoring climate change issues and how these nuclear reactors could be used to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels.
Kuosheng
Kuosheng NPP was closed for political reasons.
Taiwan’s government is committed to phasing out the use of nuclear power by 2025 and replacing it with renewable energy so that renewable energy will account for 20% of the energy mix with fossil fuels accounting for the other 80%
Because Taiwan is still using a lot of fossil fuels in its energy consumption, and because the energy produced by nuclear reactors can be used to replace fossil fuels, this decision is in total opposition with the climate commitments this country made.
Fort St. Vrain
The Fort Saint Vrain NPP was stopped for political and economic reasons The replacement cost of a part of the reactor was deemed excessive and the plant was shut down, in a context where fossil fuels are cheaper and where repairing the nuclear reactor while reducing CO2 emissions was less interesting economically and politically than just using more fossil fuels.
San Onofre
The San Onofre NPP was closed for political and economic reasons.
“it was uncertain renewal would be economic, so it made little sense making costly and politically difficult repairs now that would not make a return on investment before 2022”.
This decision was made while the US are still consuming fossil fuels, while this reactor could have helped in reducing the consumption of fossil fuels, in a context where fossil fuels where cheaper, and without considering political commitments regarding climate change.
Superphénix
Superphénix was an large-scale experimental and commercial reactor closed for political and economic reasons, in a context where fossil fuels were cheaper, without considering political commitments regarding climate change and how nuclear energy could be used to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels, and without considering the needs for research regarding all possible low-carbon energy sources.
Fessenheim
Fessenheim was closed for political reasons, as a commitment of the leading french political parties in 2012 and 2017. The reactor was deliberately not brought up to the current safety standard. In 2022 the French president justified his decision saying “Fessenheim was the oldest plant in our fleet on the border with Germany, which is not aligned with us on nuclear power”. French nuclear safety authority stated “For us, there is no reason to close this reactor”. The reactors were closed while France is still using fossil fuels, while Germany which could import the low-carbon electricity from this plant is still consuming coal and gas to produce electricity, without considering the Paris agreement, climate change issues and political commitments regarding climate change.

Tsuruga
Tsuruga 1 was closed for political and economic reasons.
JAPC said that while it would have been technically feasible to bring Tsuruga 1 up to the standards required, the size of the project and the degree of capital investment required underpinned the decommissioning decision.
The reactor was closed in a context where Japan is still using fossil fuels and could have used this nuclear reactor longer to consume less fossil fuels.
Duane Arnold
Duane Arnold NPP was closed for political and economic reasons in a context where the US are still consuming a lot of fossil fuels, without considering climate commitments and the Paris agreement.
The plant cooling towers were damaged during a derecho, and repairs were deemed uneconomical
Instead of using this low-carbon source of electricity to reduce its consumption of fossil fuels, US increased its consumption of natural gas which is responsible for CO2 and CH4 emissions. The resulting climate change will certainly be uneconomical but it wasn’t considered in the analysis at the time because it would mostly affect future generations.
Pilgrim
Pilgrim 1 was closed for economic, safety, and political reasons.
On October 13, 2015, the plant’s owners announced that it would close by June 1, 2019, citing “market conditions and increased costs,” which would have included tens of millions of dollars of necessary safety upgrades
This plant was closed in a context where fossil fuels were cheaper, yet they induce climate change and therefore create a large risk on the safety of humanity, while fossil fuels are also responsible for more than 1 million deaths per year due to fine particles. Therefore, this plant was closed without considering climate change issues and a risk hierarchy.
Yankee Rowe 1
The Yankee rowe NPP was a small reactor closed in 1991 for safety reasons:
Yankee Rowe was shut down prematurely due to reactor pressure vessel embrittlement concerns
Zion
The Zion NPP was closed for political and economic reasons:
it would have cost $435 million to order steam generators which would not pay for themselves
This decision was made in a context where fossil fuels were cheaper, without considering climate commitments.
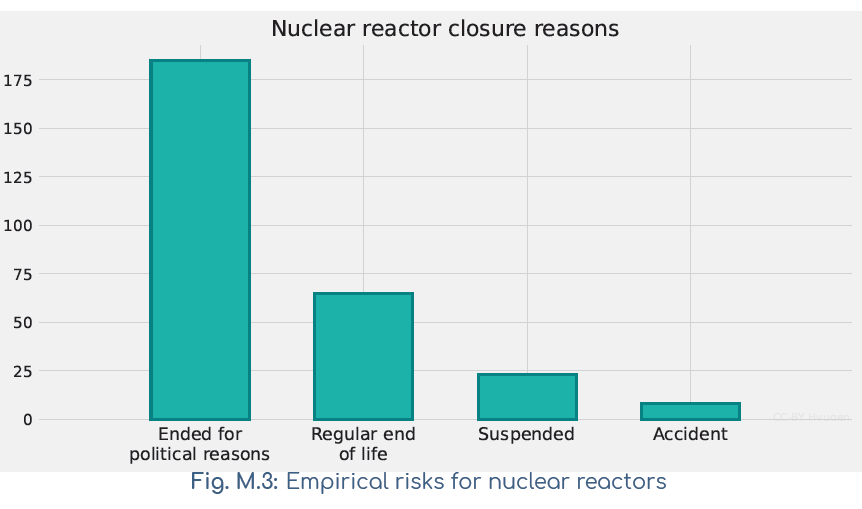
Results after reviewing hundreds of NPPs
Links
You can see how I used some of these results in the DEC report. Some of the data and models I used are also available on Github.
👏 if you liked this article and I’ll do more!